|
王耀廷,1,2Yao-Ting Wang Corie McHale,3 Xiqu Wang,3 張仲凱,4 莊裕鈞,4 柯碧蓮,2 Ognjen Š. Miljanić,*,3 陳登豪*1
|
|
1.國立成功大學藥學系School of Pharmacy, National Cheng Kung University
2.國立成功大學化學工程學系/跨維綠能材料研究中心Department of Chemical Engineering and Hierarchical Green-Energy Materials Research Center, National Cheng Kung University
3.美國休士頓大學化學系Department of Chemistry, University of Houston
4.國家同步輻射研究中心National Synchrotron Radiation Research Center
|
|

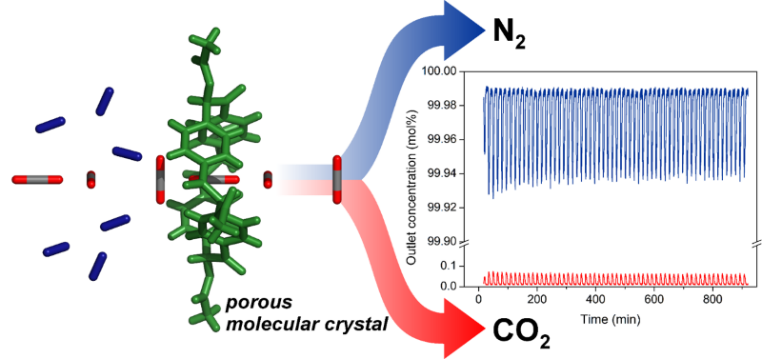
二氧化碳排放造成全球暖化是當今亟待解決之問題,以變壓吸附方式捕捉及分離二氧化碳較具能源效率,但目前所使用之吸附材料大多為分子篩,其前置處理過程繁複,材料再生耗能且分離效果有限。本實驗室與美國休士頓大學化學系Ognjen Š. Miljanić教授合作,利用其實驗室合成之孔洞分子晶體,乃由巨環分子經由弱作用力堆疊而成的有機孔洞材料,做為高效率捕捉二氧化碳的吸附劑,因其結構穩定、疏水,且再生容易,可同時達到減碳與節能,可有效降低成本。此研究為全球首次應用有機結晶性孔洞材料於變壓吸附氣體分離技術,可將含有等比例二氧化碳/氮氣或二氧化碳/甲烷混合氣體,在常溫常壓下純化至>99.9%氮氣及>99.8%甲烷,深具實際應用潛力。孔洞分子晶體較為環境友善,並能於溶液中加工製備,可回收再利用,有望應用於工業廢氣淨化以及天然氣純化。
Greenhouse effect and climate change are considered the most urgent global issues needed to be tackled, which are caused by CO2 emissions. In order to reduce the amount of CO2 released to the atmosphere, adsorption technologies based on solid adsorbents are considered a promising approach, especially when the regeneration of adsorbents is achieved by pressure reduction processes, i.e., pressure swing adsorption (PSA), which shows great potential to lower the environmental, energy, and economic costs for CO2 separations. The use of common PSA adsorbents such as molecular sieves usually needs multiple pre-treatments and energy-consuming regeneration, and exhibits limited CO2 separation performance. By collaborating with Prof. Ognjen Š. Miljanić at University of Houston, we utilize, for the first time, a porous molecular crystal (PMC), assembled by macrocyclic cyclotetrabenzoin acetate, as an efficient PSA adsorbent for CO2 separations. The eluted N2 and CH4 from N2/CO2 and CH4/CO2 mixtures are obtained with over 99.9% and 99.8% purity, respectively. The high CO2 affinity, excellent water tolerance, high structural stability, and ease of regeneration make this PMC a promising CO2 capture candidate for flue gas separation and natural gas upgrading. Most importantly, discrete organic molecules that comprise PMC are lightweight, easily synthesized, solution-processable, and recyclable, features which are essential for economic- and energy-efficient industrial-level manufacturing. Therefore, PMCs are highly promising solid adsorbents for CO2 separations.
|